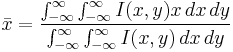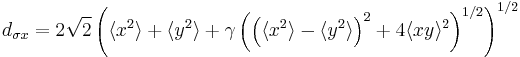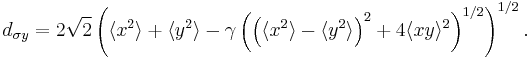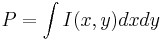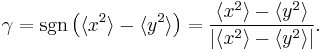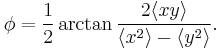Laser beam profiler
A laser beam profiler captures, displays, and records the spatial intensity profile of a laser beam at a particular plane transverse to the beam propagation path. Since there are many types of lasers — ultraviolet, visible, infrared, continuous wave, pulsed, high-power, low-power — there is an assortment of instrumentation for measuring laser beam profiles. No single laser beam profiler can handle every power level, pulse duration, repetition rate, wavelength, and beam size.
Contents
|
Overview
Laser beam profiling instruments measure the following quantities:
- Beam width: There are over five definitions of beam width.
- Beam quality: Quantified by the beam quality parameter, M2.
- Beam divergence: This is a measure of the spreading of the beam with distance.
- Beam profile: A beam profile is the 2D intensity plot of a beam at a given location along the beam path. A Gaussian or flat-top profile is often desired. The beam profile indicates nuisance high-order spatial modes in a laser cavity as well as hot spots in the beam.
- Beam astigmatism: The beam is astigmatic when the vertical and horizontal parts of the beam focus in different locations along the beam path.
- Beam wander or jitter: The amount that the centroid or peak value of the beam profile moves with time.
Instruments and techniques were developed to obtain the beam characteristics listed above. These include:
- Camera techniques: These include the direct illumination of a camera sensor. The maximum spot size that will fit onto a CCD sensor is on the order of 10 mm. Alternatively, illuminating a flat diffuse surface with the laser and imaging the light onto a CCD with a lens allows profiling of larger-diameter beams. Viewing lasers off diffuse surfaces is excellent for large beam widths but requires a diffuse surface that has uniform reflectivity (<1% variation) over the illuminated surface.
- Knife-edge technique: A spinning blade or slit cuts the laser beam before detection by a power meter. The power meter measures the intensity as a function of time. By taking the integrated intensity profiles in a number of cuts, the original beam profile can be reconstructed using algorithms developed for tomography. This usually does not work for pulsed lasers, and does not provide a true 2D beam profile, but it does have excellent resolution, in some cases <1 µm.
- Phase-front technique: The beam is passed through a 2D array of tiny lenses in a Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor. Each lens will redirect its portion of the beam, and from the position of the deflected beamlet, the phase of the original beam can be reconstructed.
- Historical techniques: These include the use of photographic plates and burn plates. For example, high-power carbon dioxide lasers were profiled by observing slow burns into acrylate blocks.
As of 2002[update], commercial knife-edge measurement systems cost $5,000–$12,000 USD and CCD beam profilers cost $4,000–9,000 USD.[1] The cost of CCD beam profilers has come down in recent years, primarily driven by lower silicon CCD sensor costs, and as of 2008[update] they can be found for less than $1000 USD.
Applications
The applications of laser beam profiling include:
- Laser cutting: A laser with an elliptical beam profile has a wider cut along one direction than along the other. The width of the beam influences the edges of the cut. A narrower beam width yields high fluence and ionizes, rather than melts, the machined part. Ionized edges are cleaner and have less knurling than melted edges.
- Nonlinear optics: Frequency conversion efficiency in nonlinear optical materials is proportional to the square (sometimes cubed or more) of the input light intensity. Therefore, to get efficient frequency conversion, the input beam waist must be as small as possible. A beam profiler can help minimize the beam waist in the nonlinear crystal.
- Alignment: Beam profilers align beams with orders of magnitude better angular accuracy than irises.
- Laser monitoring: It is often necessary to monitor the laser output to see whether the beam profile changes after long hours of operation. Maintaining a particular beam shape is critical for adaptive optics, nonlinear optics, and laser-to-fiber delivery. In addition, laser status can be measured by imaging the emitters of a pump diode laser bar and counting the number of emitters that have failed or by placing several beam profilers at various points along a laser amplifier chain.
- Laser and laser amplifier development: Thermal relaxation in pulse-pumped amplifiers causes temporal and spatial variations in the gain crystal, effectively distorting the beam profile of the amplified light. A beam profiler placed at the output of the amplifier yields a wealth of information about transient thermal effects in the crystal. By adjusting the pump current to the amplifier and tuning the input power level, the output beam profile can be optimized in real-time.
- Far-field measurement: It is important to know the beam profile of a laser for laser radar or free-space optical communications at long distances, the so-called “far-field.” The width of the beam in its far-field determines the amount of energy collected by a communications receiver and the amount of energy incident on the ladar’s target. Measuring the far-field beam profile directly is often impossible in a laboratory because of the long path length required. A lens, on the other hand, transforms the beam so that the far-field occurs near its focus. A beam profiler placed near the focus of the lens measures the far-field beam profile in significantly less benchtop space.
- Education: Beam profilers can be used for student laboratories to verify diffraction theories and test the Fraunhofer or Fresnel diffraction integral approximations. Other student laboratory ideas include using a beam profiler to measure Poisson’s spot of an opaque disk and to map out the Airy disk diffraction pattern of a clear disk.
Measurements
Beam width
The beam width is the single most important characteristic of a laser beam profile. At least five definitions of beam width are in common use: D4σ, 10/90 or 20/80 knife-edge, 1/e2, FWHM, and D86. The D4σ beam width is the ISO standard definition and the measurement of the M² beam quality parameter requires the measurement of the D4σ widths.[2][3][4] The other definitions provide complementary information to the D4σ and are used in different circumstances. The choice of definition can have a large effect on the beam width number obtained, and it is important to use the correct method for any given application.[5] The D4σ and knife-edge widths are sensitive to background noise on the detector, while the 1/e2 and FWHM widths are not. The fraction of total beam power encompassed by the beam width depends on which definition is used.
D4σ or second moment width
D4σ is shorthand for the diameter that is 4 times σ, where σ is the standard deviation of the horizontal or vertical marginal distribution. Mathematically, the D4σ beam width in the x-dimension for the beam profile  is expressed as
is expressed as
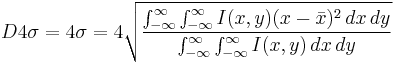 ,
,
where
is the centroid of the beam profile in the x-direction. The wings of the beam profile influence the D4σ value more than the center of the beam profile since the wings of the marginal distribution are weighted by the square of its distance, x2, from the center of the beam. If the beam does not fill more than a third of the beam profiler’s sensor area, then there will be a significant number of pixels at the edges of the sensor that register a small baseline value (the background value). If the baseline value is large or if it is not subtracted out of the image, then the computed D4σ value will be larger than the actual value because the baseline value near the edges of the sensor are weighted in the D4σ integral by x2. Therefore, baseline subtraction is necessary for accurate D4σ measurements. The baseline is easily measured by recording the average value for each pixel when the sensor is not illuminated. The D4σ width, unlike the FWHM and 1/e2 widths, is meaningful for multimodal marginal distributions — that is, beam profiles with multiple peaks — but requires careful subtraction of the baseline for accurate results. The D4σ is the ISO international standard definition for beam width.
ISO11146 beam width for elliptic beams[4]
The definition given before holds for stigmatic (circular symmetric) beams only. For astigmatic beams however, a more rigorous definition of the beam width has to be used,
and
This definition also incorporates information about x-y-correlation 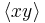 , but for circular symmetric beams, both definitions are the same.
, but for circular symmetric beams, both definitions are the same.
Some new symbols appeared within the formulas, which are the first- and second-order moments
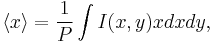
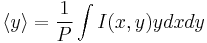 and
and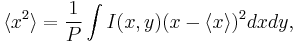
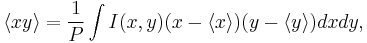
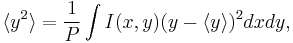
the beam power
and
Using this general definition, also the beam's azimutal-angle  can be expressed. It is the angle between the beam's directions of minimum and maximum elongation, known as principal axis, and the laboratory system, being the
can be expressed. It is the angle between the beam's directions of minimum and maximum elongation, known as principal axis, and the laboratory system, being the  - and
- and 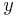 -axis of the detector and given by
-axis of the detector and given by
Knife-edge width
Before the advent of the CCD beam profiler, the beam width was estimated using the knife-edge technique. The technique is as follows: slice a laser beam with a razor and measure the power of the clipped beam as a function of the razor position. The measured curve is the integral of the marginal distribution, and starts at the total beam power and decreases monotonically to zero power. The width of the beam is defined as either the distance between the points of the measured curve that are 10% and 90% (or 20% and 80%) of the maximum value. If the baseline value is small or subtracted out, the knife-edge beam width always corresponds to 60%, in the case of 20/80, or 80%, in the case of 10/90, of the total beam power no matter what the beam profile. On the other hand, the D4σ, 1/e2, and FWHM widths encompass fractions of power that are beam-shape dependent. Therefore, the 10/90 or 20/80 knife-edge width is a useful metric when the user wishes to be sure that the width encompasses a fixed fraction of total beam power. Most CCD beam-profiler software can compute the knife-edge width numerically.
1/e2 width
The 1/e2 width is equal to the distance between the two points on the marginal distribution that are 1/e2 = 0.135 times the maximum value. If there are more than 2 points that are 1/e2 times the maximum value, then the two points closest to the maximum are chosen. The 1/e2 width only depends on 3 points on the marginal distribution, unlike D4σ and knife-edge widths that depend on the integral of the marginal distribution. 1/e2 width measurements are noisier than D4σ width measurements for each collected CCD frame. For multimodal marginal distributions (a beam profile with multiple peaks), the 1/e2 width usually does not yield a meaningful value and can grossly underestimate of the inherent width of the beam. For multimodal distributions, a D4σ width would be a better choice.
The American National Standard Z136.1-2007 for Safe Use of Lasers (p. 6) defines the beam diameter as the distance between diametrically opposed points in that cross-section of a beam where the power per unit area is 1/e (0.368) times that of the peak power per unit area. This is the beam diameter definition that is used for computing the maximum permissible exposure to a laser beam. In addition, the Federal Aviation Administration also uses the 1/e definition for laser safety calculations in FAA Order 7400.2F, "Procedures for Handling Airspace Matters," February 16, 2006, p. 29-1-2.
D86 width
The D86 width is defined as the diameter of the circle that is centered at the centroid of the beam profile and contains 86% of the beam power. The solution for D86 is found by computing the area of increasingly larger circles around the centroid until the area contains 0.86 of the total power. Unlike the previous beam width definitions, the D86 width is not derived from marginal distributions. The strange percentage of 86, rather than 50, 80, or 90, is chosen because a circular Gaussian beam profile integrated down to 1/e2 of its peak value contains 86% of its total power. The D86 width is often used in applications that are concerned with knowing exactly how much power is in a given area. For example, high-energy laser weapons and ladars are two applications that require precise knowledge of how much transmitted power actually illuminates the target.
Beam quality
Beam quality parameter, M2
The M2 parameter is a measure of beam quality; a low M2 value indicates good beam quality and ability to be focused to a tight spot. The value M is equal to the ratio of the beam’s angle of divergence to that of a Gaussian beam with the same D4σ waist width. Since the Gaussian beam diverges more slowly than any other beam shape, the M2 parameter is always greater than or equal to one. Other definitions of beam quality have been used in the past, but the one using second moment widths is most commonly accepted.[6]
Beam quality is important in many applications. In fiber-optic communications beams with an M2 close to 1 are required for coupling to single-mode optical fiber. Laser machine shops care a lot about the M2 parameter of their lasers because the beams will focus to an area that is M2 times larger than that of a Gaussian beam with the same wavelength and D4σ waist width; in other words, the fluence scales as 1/M2. The general rule of thumb is that M2 increases as the laser power increases. It is difficult to obtain excellent beam quality and high average power (100 W to kWs) due to thermal lensing in the laser gain medium.
The M2 parameter is determined experimentally as follows:[2]
- Measure the D4σ widths at 5 axial positions near the beam waist (the location where the beam is narrowest).
- Measure the D4σ widths at 5 axial positions at least one Rayleigh length away from the waist.
- Fit the 10 measured data points to
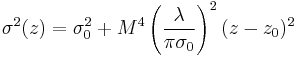 ,[7] where
,[7] where 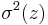 is the second moment of the distribution in the x or y direction (see section on D4σ beam width), and
is the second moment of the distribution in the x or y direction (see section on D4σ beam width), and 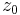 is the location of the beam waist with second moment width of
is the location of the beam waist with second moment width of 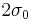 . Fitting the 10 data points yields M2,
. Fitting the 10 data points yields M2, 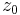 , and
, and 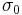 . Siegman showed that all beam profiles — Gaussian, flat top, TEMXY, or any shape — must follow the equation above provided that the beam radius uses the D4σ definition of the beam width. Using the 10/90 knife-edge, the D86, or the FWHM widths does not work.
. Siegman showed that all beam profiles — Gaussian, flat top, TEMXY, or any shape — must follow the equation above provided that the beam radius uses the D4σ definition of the beam width. Using the 10/90 knife-edge, the D86, or the FWHM widths does not work.
Complete E-field beam profiling
Beam profilers measure the intensity, |E-field|2, of the laser beam profile but do not yield any information about the phase of the E-field. To completely characterize the E-field at a given plane, both the phase and amplitude profiles must be known. The real and imaginary parts of the electric field can be characterized using two CCD beam profilers that sample the beam at two separate propagation planes, with the application of a phase recovery algorithm to the captured data. The benefit of completely characterizing the E-field in one plane is that the E-field profile can be computed for any other plane with diffraction theory.
Power-in-the-bucket or Strehl definition of beam quality
The M2 parameter is not the whole story in specifying beam quality. A low M2 only implies that the second moment of the beam profile expands slowly. Nevertheless, two beams with the same M2 may not have the same fraction of delivered power in a given area. Power-in-the-bucket and Strehl ratio are two attempts to define beam quality as a function of how much power is delivered to a given area. Unfortunately, there is no standard bucket size (D86 width, Gaussian beam width, Airy disk nulls, etc.) or bucket shape (circular, rectangular, etc.) and there is no standard beam to compare for the Strehl ratio. Therefore, these definitions must always be specified before a number is given and it presents much difficulty when trying to compare lasers. There is also no simple conversion between M2, power-in-the-bucket, and Strehl ratio. The Strehl ratio, for example, has been defined as the ratio of the peak focal intensities in the aberrated and ideal point spread functions. In other cases, it has been defined as the ratio between the peak intensity of an image divided by the peak intensity of a diffraction-limited image with the same total flux.[8][9] Since there are many ways power-in-the-bucket and Strehl ratio have been defined in the literature, the recommendation is to stick with the ISO-standard M2 definition for the beam quality parameter and be aware that a Strehl ratio of 0.8, for example, does not mean anything unless the Strehl ratio is accompanied by a definition.
Beam divergence
The beam divergence of a laser beam is a measure for how fast the beam expands far from the beam waist. It is usually defined as the derivative of the beam radius with respect to the axial position in the far field, i.e., in a distance from the beam waist which is much larger than the Rayleigh length. This definition yields a divergence half-angle. (Sometimes, full angles are used in the literature; these are twice as large.) For a diffraction-limited Gaussian beam, the beam divergence is λ/(πw0), where λ is the wavelength (in the medium) and w0 the beam radius (radius with 1/e2 intensity) at the beam waist. A large beam divergence for a given beam radius corresponds to poor beam quality. A low beam divergence can be important for applications such as pointing or free-space optical communications. Beams with very small divergence, i.e., with approximately constant beam radius over significant propagation distances, are called collimated beams. For the measurement of beam divergence, one usually measures the beam radius at different positions, using e.g. a beam profiler. It is also possible to derive the beam divergence from the complex amplitude profile of the beam in a single plane: spatial Fourier transforms deliver the distribution of transverse spatial frequencies, which are directly related to propagation angles. See US Laser Corps application note[10] for a tutorial on how to measure the laser beam divergence with a lens and CCD camera.
Beam astigmatism
Astigmatism in a laser beam occurs when the horizontal and vertical cross sections of the beam focus at different locations along the beam path. Astigmatism can be corrected with a pair of cylindrical lenses. The metric for astigmatism is the power of cylindrical lens needed to bring the focuses of the horizontal and vertical cross sections together. Astigmatism is caused by:
- Thermal lensing in Nd:YAG slab amplifiers. A slab that is sandwiched between two metal heat sinks will have a temperature gradient between the heat sinks. The thermal gradient causes an index of refraction gradient that is very similar to a cylindrical lens. The cylindrical lensing caused by the amplifier will make the beam astigmatic.
- Unmatched cylindrical lenses or error in placement of these optics.
- Propagation through a nonlinear uniaxial crystal (common in nonlinear optic crystals). The x- and y-polarized E-fields experience different refractive indices.
- Not propagating through the center of a spherical lens or mirror.
Astigmatism can easily be characterized by a CCD beam profiler by observing where the x and y beam waists occur as the profiler is translated along the beam path.
Beam wander or jitter
Every laser beam wanders and jitters — albeit a small amount. The typical kinematic tip-tilt mount drifts by around 100 μrad per day in a laboratory environment (vibration isolation via optical table, constant temperature and pressure, and no sunlight that causes parts to heat). A laser beam incident upon this mirror will be translated by 100 m at a range of 1000 km. This could make the difference between hitting or not hitting a communications satellite from Earth. Hence, there is a lot of interest in characterizing the beam wander (slow time scale) or jitter (fast time scale) of a laser beam. The beam wander and jitter can be measured by tracking the centroid or peak of the beam on a CCD beam profiler. The CCD frame rate is typically 30 frames per second and therefore can capture beam jitter that is slower than 30 Hz — it can’t see fast vibrations due to one’s voice, 60 Hz fan motor hum, or other sources of fast vibrations. Fortunately, this is usually not a great concern for most laboratory laser systems and the frame rates of CCDs are fast enough to capture the beam wander over the bandwidth that contains the greatest noise power. A typical beam wander measurement involves tracking the centroid of the beam over several minutes. The rms deviation of the centroid data gives a clear picture of the laser beam pointing stability. The integration time of the beam jitter measurement should always accompany the computed rms value. Even though the pixel resolution of a camera may be several micrometres, sub-pixel centroid resolution (possibly tens of nanometer resolution) is attained when the signal to noise ratio is good and the beam fills most of the CCD active area.[11]
Beam wander is caused by:
- Slow thermalization of the laser. Laser manufacturers usually have a warm-up specification to allow the laser to drift to an equilibrium after startup.
- Tip-tilt and optical mount drift caused by thermal gradients, pressure, and loosening of springs.
- Non-rigidly mounted optics — by accident of course!
- Vibration due to fans, people walking/sneezing/breathing, water pumps, and movement of vehicles outside the laboratory.
Misrepresentation of beam profiler measurements for laser systems
It is to most laser manufacturers' advantage to present specifications in a way that shows their product in the best light, even if this involves misleading the customer. Laser performance specifications can be clarified by asking questions such as:
- Is the specification typical or worst-case performance?
- What beam width definition was used?
- Is the M2 parameter for both vertical and horizontal cross sections, or just for the better cross section?
- Was M2 measured using the ISO-standard technique or some other way — e.g. power in the bucket.
- Over how long was the data taken to come up with the specified rms beam jitter. (RMS beam jitter gets worse as the measurement interval increases.) What was the laser environment (optical table, etc.)?
- What is the warm-up time needed to achieve the specified M2, beam width, divergence, astigmatism, and jitter?
Techniques
Beam profilers generally fall into two classes: the first uses a simple photodetector behind an aperture which is scanned over the beam. The second class uses a camera to image the beam.
Scanning-aperture techniques
The most common scanning aperture techniques are the knife-edge technique and the scanning-slit profiler. The former chops the beam with a knife and measures the transmitted power as the blade cuts through the beam. The measured intensity versus knife position yields a curve that is the integrated beam intensity in one direction. By measuring the intensity curve in several directions, the original beam profile can be reconstructed using algorithms developed for x-ray tomography. Tomographic laser beam profilers were originally developed as a measuring instrument by Duma Optronics . The measuring instrument is based on high precision multiple knife edges each deployed on a rotating drum and having a different angle with respect to beam orientation. Scanned beam is than reconstructed using tomographic algorithms and provides 2D or 3D high resolution energy distribution plots. Because of the special scanning technique the system automatically zooms in onto the current beam size enabling high resolution measurements of sub micron beams as well as relative large beams of 10 or more millimeters.To obtain measurement of various wavelength different detectors are used to allow laser beam measurements from deep UV to far IR. Unlike other camera based systems this technology also provides accurate power measurement in real time Scanning-slit profilers use a narrow slit instead of a single knife edge. In this case, the intensity is integrated over the slit width. The resulting measurement is equivalent to the original cross section convolved with the profile of the slit.
These techniques can measure very small spot sizes down to 1 μm, and can be used to directly measure high power beams. They do not offer continuous readout, although repetition rates as high as twenty hertz can be achieved. Also, the profiles give integrated intensities in the x and y directions and not the actual 2D spatial profile (integrating intensities can be hard to interpret for complicated beam profiles). They do not generally work for pulsed laser sources, because of the extra complexity of synchronizing the motion of the aperture and the laser pulses.
CCD camera technique
The CCD camera technique is simple: attenuate and shine a laser onto a CCD and measure the beam profile directly. It is for this reason that the camera technique is the most popular method for laser beam profiling. The most popular cameras used are silicon CCDs that have sensor diameters that range up to 25 mm (1 inch) and pixel sizes down to a few micrometres. These cameras are also sensitive to a broad range of wavelengths, from deep UV, 200 nm, to near infrared, 1100 nm; this range of wavelengths encompass a broad range of laser gain media. The advantages of the CCD camera technique are:
- It captures the 2D beam profile in real-time
- Software typically displays critical beam metrics, such as D4σ width, in real-time
- Sensitive CCD detectors can capture the beam profiles of weak lasers
- Resolution down to about 4 μm
- CCD cameras with trigger inputs can be used to capture beam profiles of low-duty-cycle pulsed lasers
- CCD’s have broad wavelength sensitivities from 200 to 1100 nm
The disadvantages of the CCD camera technique are that attenuation is required for high power lasers, and CCD sensor size limited to about 1 inch.
Baseline subtraction for D4σ width measurements
The D4σ width is sensitive to the beam energy or noise in the tail of the pulse because the pixels that are far from the beam centroid contribute to the D4σ width as the distance squared. To reduce the error in the D4σ width estimate, the baseline pixel values are subtracted from the measured signal. The baseline values for the pixels are measured by recording the values of the CCD pixels with no incident light. The finite value is due to dark current, readout noise, and other noise sources. For shot-noise-limited noise sources, baseline subtraction improves the D4σ width estimate as 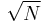 , where
, where 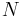 is the number of pixels in the wings. Without baseline subtraction, the D4σ width is overestimated.
is the number of pixels in the wings. Without baseline subtraction, the D4σ width is overestimated.
Averaging to get better measurements
Averaging consecutive CCD images yields a cleaner profile and removes both CCD imager noise and laser beam intensity fluctuations. The signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) of a pixel for a beam profile is defined as the mean value of the pixel divided by its root-mean-square (rms) value. The SNR improves as square root of the number of captured frames for shot noise processes – dark current noise, readout noise, and Poissonian detection noise. So, for example, increasing the number of averages by a factor of 100 smooths out the beam profile by a factor of 10.
Attenuation techniques
Since CCD sensors are highly sensitive, attenuation is almost always needed for proper beam profiling. For example, 40 dB (ND 4 or 10−4) of attenuation is typical for a milliwatt HeNe laser. Proper attenuation has the following properties:
- It does not result in multiple reflections leaving a ghost image on the CCD sensor
- It does not result in interference fringes due to reflections between parallel surfaces or diffraction by defects
- It does not distort the wavefront and will be an optical element with sufficient optical flatness (less than one tenth of a wavelength) and homogeneity
- It can handle the required optical power
For laser beam profiling with CCD sensors, typically two types of attenuators are used: neutral density filters, and wedges or thick optical flats.
Neutral density filters
Neutral density (ND) filters come in two types: absorptive and reflective. Absorptive filters (for example made of Schott 1234 glass) are for lower-power applications that involve up to about 100 mW average power. Above those power levels, one risks melting the filter. Absorptive filter attenuation values are valid for the visible spectrum (500–700 nm) and are not valid outside of that spectral region. Typically, one can expect about 5-10% variation of the attenuation across a 2-inch (51 mm) ND filter, unless specified otherwise to the manufacturer. The attenuation values of ND filters are specified logarithmically. A ND 3 filter transmits 10−3 of the incident beam power. Placing the largest attenuator last before the CCD sensor will result in the best rejection of ghost images due to multiple reflections. Reflective filters are made with a thin metallic coating and hence operate over a larger bandwidth. An ND 3 metallic filter will be good over 200–2000 nm. The attenuation will rapidly increase outside this spectral region. These filters reflect rather than absorb the incident power, and hence can handle higher input average powers. However, they are less well suited to the high peak powers of pulsed lasers. These filters work fine to about 5 W average power (over about 1 cm2 illumination area) before heating causes them to crack. Since these filters reflect light, one must be careful when stacking multiple ND filters, since multiple reflections among the filters will cause a ghost image to interfere with the original beam profile. One way to mitigate this problem is by tilting the ND filter stack. Assuming that the absorption of the metallic ND filter is negligible, the order of the ND filter stack doesn’t matter, as it does for the absorptive filters.
Optical wedges
Optical wedges and reflections from uncoated optical glass surfaces are used to attenuate high power laser beams. About 4% is reflected from the air/glass interface and several wedges can be used to greatly attenuate the beam to levels that can be attenuated with ND filters. The angle of the wedge is typically selected so that the second reflection from the surface does not hit the active area of the CCD, and that no interference fringes are visible. The farther the CCD is from the wedge, the smaller the angle required. Wedges have the disadvantage of both translating and bending the beam direction — paths will no longer lie on convenient rectangular coordinates. Rather than using a wedge, an optical-quality thick glass plate tilted to the beam can also work — actually, this is the same as a wedge with a 0° angle. The thick glass will translate the beam but it will not change the angle of the output beam. The glass must be thick enough so that the beam does not overlap with itself to produce interference fringes, and if possible that the secondary reflection does not illuminate the active area of the CCD. The Fresnel reflection of a beam from a glass plate is different for the s- and p-polarizations (s is parallel to the surface of the glass, and p is perpendicular to s) and changes as a function of angle of incidence – keep this in mind if you expect that the two polarizations have different beam profiles. To prevent distortion of the beam profile, the glass should be of optical quality — surface flatness of λ/10 (λ=633 nm) and scratch-dig of 40-20 or better. A half-wave plate followed by a polarizing beam splitter form a variable attenuator and this combination is often used in optical systems. The variable attenuator made in this fashion is not recommended for attenuation for beam profiling applications because: (1) the beam profile in the two orthogonal polarizations may be different, (2) the polarization beam cube may have a low optical damage threshold value, and (3) the beam can be distorded in cube polarizers at very high attenuation. Inexpensive cube polarizers are formed by cementing two right angle prisms together. The glue does not stand up well to high powers — the intensity should be kept under 500 mW/mm2. Single-element polarizers are recommended for high powers.
Optimal beam size on the CCD detector
There are two competing requirements that determine the optimal beam size on the CCD detector. One requirement is that the entire energy — or as much of it as possible — of the laser beam is incident on the CCD sensor. This would imply that we should focus all the energy in the center of the active region in as small a spot as possible using only a few of the central pixels to ensure that the tails of the beam are captured by the outer pixels. This is one extreme. The second requirement is that we need to adequately sample the beam profile shape. As a general rule of thumb, we want at least 10 pixels across the area that encompasses most, say 80%, of the energy in the beam. Therefore, there is no hard and fast rule to select the optimal beam size. As long as the CCD sensor captures over 90% of the beam energy and has at least 10 pixels across it, the beam width measurements will have some accuracy.
Pixel size and number of pixels
The larger the CCD sensor, the larger the size of beam that can be profiled. Sometimes this comes at the cost of larger pixel sizes. Small pixels sizes are desired for observing focused beams. A CCD with many megapixels is not always better than a smaller array since readout times on the computer can be uncomfortably long. Reading out the array in real-time is essential for any tweaking or optimization of the laser profile.
Far-field beam profiler
A far-field beam profiler is nothing more than profiling the beam at the focus of a lens. This plane is sometimes called the Fourier plane and is the profile that one would see if the beam propagated very far away. The beam at the Fourier plane is the Fourier transform of the input field. Care must be taken in setting up a far-field measurement. The focused spot size must be large enough to span across several pixels. The spot size is approximately fλ/D, where f is the focal length of the lens, λ is the wavelength of the light, and D is the diameter of the collimated beam incident upon the lens. For example, a helium-neon laser (633 nm) with 1 mm beam diameter would focus to a 317 μm spot with a 500 mm lens. A laser beam profiler with a 5.6 μm pixel size would adequately sample the spot at 56 locations.
Special applications
The prohibitive costs of CCD laser beam profilers in the past have given way to low-cost beam profilers. Low-cost beam profilers have opened up a number of new applications: replacing irises for super-accurate alignment and simultaneous multiple port monitoring of laser systems.
Iris replacement with microradian alignment accuracy
In the past, alignment of laser beams was done with irises. Two irises uniquely defined a beam path; the farther apart the irises and the smaller the iris holes, the better the path was defined — that is, only a few light rays could be drawn through both irises. The smallest aperture that an iris can define is about 0.8 mm. In comparison, the centroid of a laser beam can be determined to sub-micrometre accuracy with a laser beam profiler. The laser beam profiler's effective aperture size is three orders of magnitude smaller than that of an iris. Consequently, the ability to define an optical path is 1000 times better when using beam profilers over irises. Applications that need microradian alignment accuracies include earth-to-space communications, earth-to-space ladar, master oscillator to power oscillator alignment, and multi-pass amplifiers.
Simultaneous multiple port monitoring of laser system
Experimental laser systems benefit from the use of multiple laser beam profilers to characterize the pump beam, the output beam, and the beam shape at intermediate locations in the laser system, for example, after a Kerr-lens modelocker. Changes in the pump laser beam profile indicate the health of the pump laser, which laser modes are excited in the gain crystal, and also determine whether the laser is warmed up by locating the centroid of the beam relative to the breadboard. The output beam profile is often a strong function of pump power due to thermo-optical effects in the gain medium.
References
- ^ R. Bolton, "Give your laser beam a checkup," Photonics Spectra, June 2002. Table 1.
- ^ a b ISO 11146-1:2005(E), "Lasers and laser-related equipment — Test methods for laser beam widths, divergence angles and beam propagation ratios — Part 1: Stigmatic and simple astigmatic beams."
- ^ ISO 11146-2:2005(E), "Lasers and laser-related equipment — Test methods for laser beam widths, divergence angles and beam propagation ratios — Part 2: General astigmatic beams."
- ^ a b ISO 11146-1:2005(E), "Lasers and laser-related equipment — Test methods for laser beam widths, divergence angles and beam propagation ratios — Part 3: Intrinsic and geometrical laser beam classification, propagation and details of test methods."
- ^ Ankron. "Standard definition of beam width" Technical Note, 13 Sep 2008,
- ^ A. E. Siegman, "How to (Maybe) Measure Laser Beam Quality," Tutorial presentation at the Optical Society of America Annual Meeting Long Beach, California, October 1997.
- ^ A. E. Siegman, "How to (Maybe) Measure Laser Beam Quality," Tutorial presentation at the Optical Society of America Annual Meeting Long Beach, California, October 1997, p.9.
- ^ M. Born and E. Wolf, Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light, 6th edition, Cambridge University Press, 1997.
- ^ Strehl meter W.M. Keck Observatory.
- ^ Measuring laser beam divergence US Laser Corps application note
- ^ Ankron. "Technical Note 5: How to measure beam jitter with nanometer accuracy using a CCD sensor with 5.6 μm pixel size".